YAAA Code Generator (YAAAC)
Generate code and artifacts from your ADAS / AD system model
The YAAA Code Generator (YAAAC) is a command line tool to generate all middleware related source code and configuration files which are required to build and deploy a YAAA application described by the YAAA model and the functional user code. The generated files are dependent on the selected middleware type/middleware version and include in particular for the CARMA middleware the following code artifacts:
- Proxy and skeleton header files required for the publish subscribe communication mechanism
- Main files for the modeled activities, ECU local scheduling components, and inter ECU communication gateways
- Manifest files and startup scripts for the runtime configuration
The generated source code files and the functional user code are then compiled and linked together for a selected target architecture resulting in suitable executables ready to be deployed to and executed on the target hardware. An overview of the YAAAC workflow is depicted in the following image:
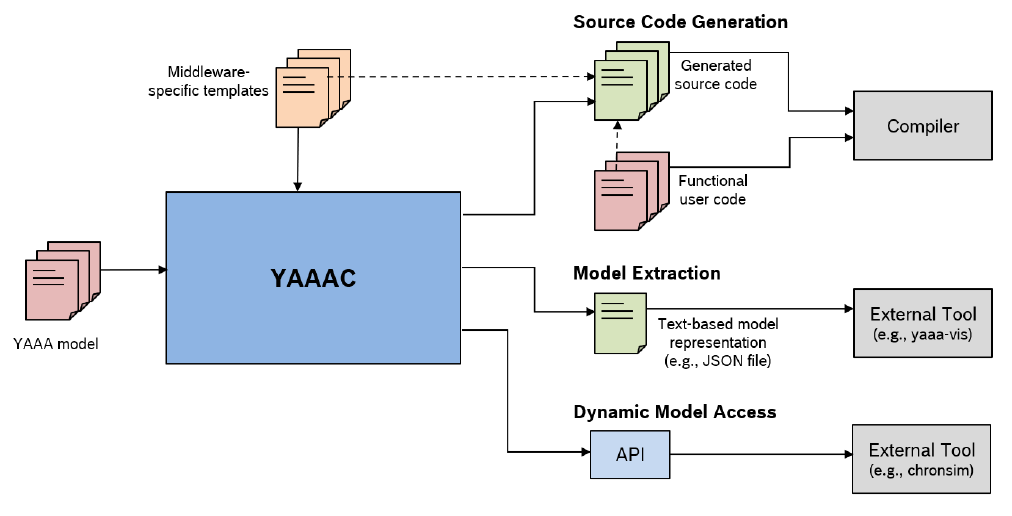
Besides code generation, YAAAC is also used to make the internal representation of the loaded YAAA model accessible to other external tools either by exporting the model to a text based representation or by providing dynamic access to the model via a Python API. In both cases, an external tool can access the complete model content such as the described software architecture, hardware architecture, or the deployment information. One example of an external tool consuming the model information via text based export is YAAA-Vis, which is used to generate a graphical representation of the software as well the hardware architecture, either as static SVG image or as interactive HTML page.
YAAAC is developed in Python technology and works similar to a compiler with a separation of the functionality into front end and back end . At the front end part, it loads and parses the YAAA model represented by a set of YAML files describing the architectural components of a YAAA application as described in the YAAA Language section. It performs model validation and preprocessing steps and creates an intermediate representation of the YAAA model, which is then consumed by the back end part for further processing. The back end part is organized by the help of a plugin interface to conveniently handle code generation for different middleware types/middleware versions and to allow users to access the internal representation via a defined API to implement user specific functionality.